ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a network protocol used to find out the hardware (MAC) address of a device from an IP address. It is used when a device wants to communicate with some other device on a local network (for example on an Ethernet network that requires physical addresses to be known before sending packets). The sending device uses ARP to translate IP addresses to MAC addresses. The device sends an ARP request message containing the IP address of the receiving device. All devices on a local network segment see the message, but only the device that has that IP address responds with the ARP reply message containing its MAC address. The sending device now has enough information to send the packet to the receiving device.
The terms address resolution refers to the process of finding an address of a computer in a network. The address is "resolved" using a protocol in which a piece of information is sent by a client process executing on the local computer to a server process executing on a remote computer. The information received by the server allows the server to uniquely identify the network system for which the address was required and therefore to provide the required address. The address resolution procedure is completed when the client receives a response from the server containing the required address.
There are four types of arp messages that may be sent by the arp protocol. These are identified by four values in the "operation" field of an arp message. The types of message are:
- ARP request
- ARP reply
- RARP request
- RARP reply
We can see this in this graphic, courtesy of practical networking .net
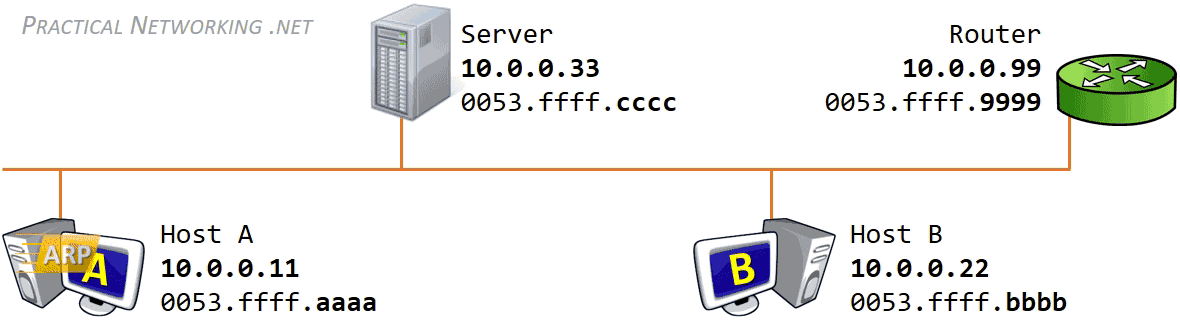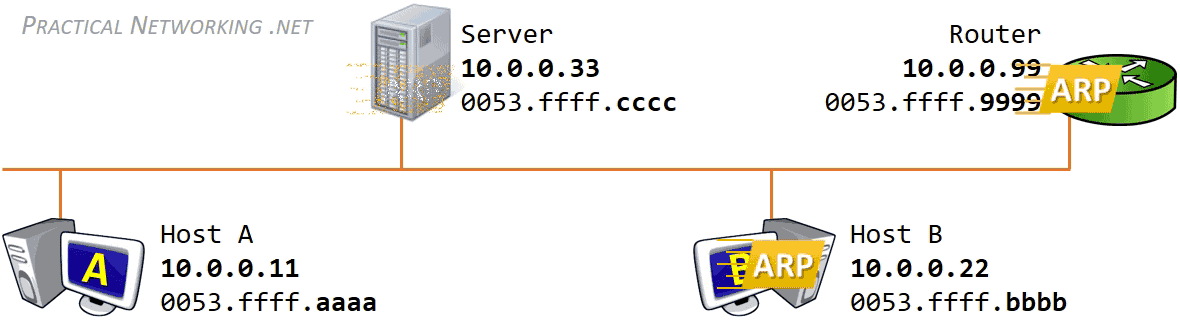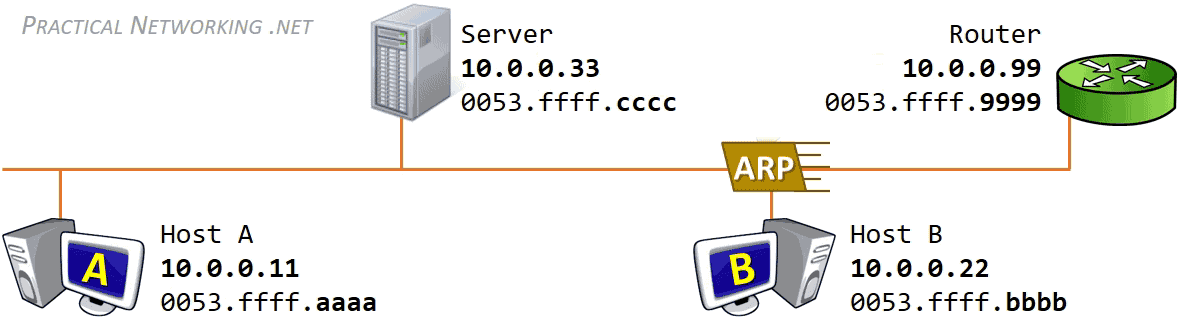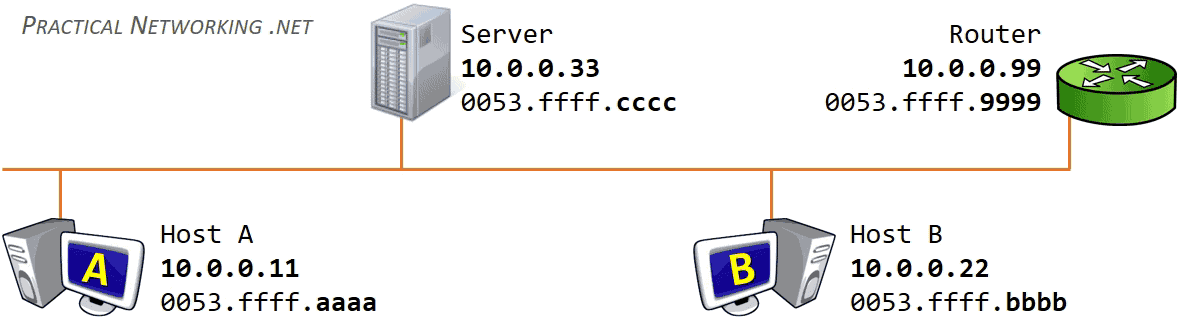

ARP
![ARP]() Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
9:12 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
9:12 AM
Rating:







No comments: